$235.00 – $1,900.00Price range: $235.00 through $1,900.00
Synthetic cannabinoids refer to a diverse class of substances designed to mimic the effects of natural cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. These compounds interact with the endocannabinoid system of the body, producing various psychoactive effects that can range from mild euphoria to intense hallucinations. The development of synthetic cannabinoids began in the 1980s, primarily for research and therapeutic purposes. However, as the popularity of cannabis surged, an increasing number of these synthetic formulations emerged in the illicit drug market, often marketed as “legal highs” or “herbal incense.” This evolution has cultivated an ever-expanding array of designer drugs that continue to pose significant challenges to public health and safety.
Among the various classes of synthetic cannabinoids, indazole-based compounds have gained considerable attention. Indazole, a five-membered heterocyclic structure, is increasingly incorporated into cannabinoid formulations due to its ability to bind effectively to cannabinoid receptors. This characteristic contributes to the potency and pharmacological effects observed with these synthetic alternatives. As researchers and illicit manufacturers explore new chemical modifications, the complexity surrounding indazole-based synthetic cannabinoids, such as 5-CL-ADB-A, continues to grow, further complicating detection and regulation efforts.
The appeal of synthetic cannabinoids, particularly among users, can be attributed to several factors. These substances are often perceived as a legal alternative to traditional cannabis; they may provide a more potent experience while evading drug testing protocols. Moreover, their availability in local shops or online platforms has made them readily accessible to a wide audience. However, this accessibility raises significant concerns regarding safety and legality. Many synthetic cannabinoids lack adequate research into their health impacts and potential risks, leading to unpredictable and often harmful effects on users.
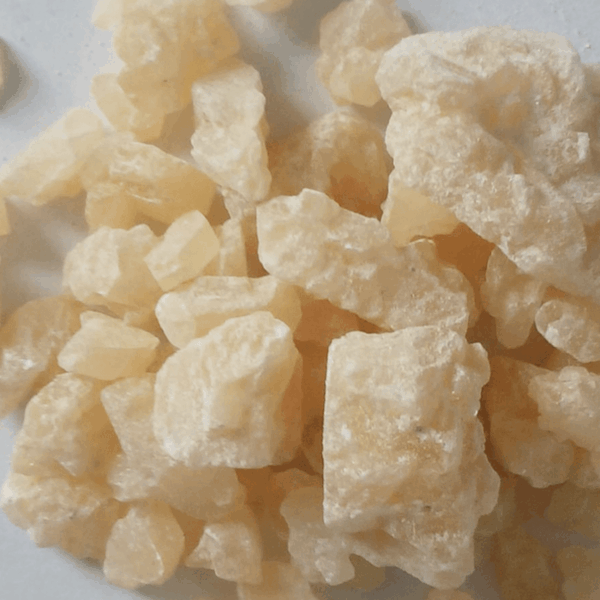
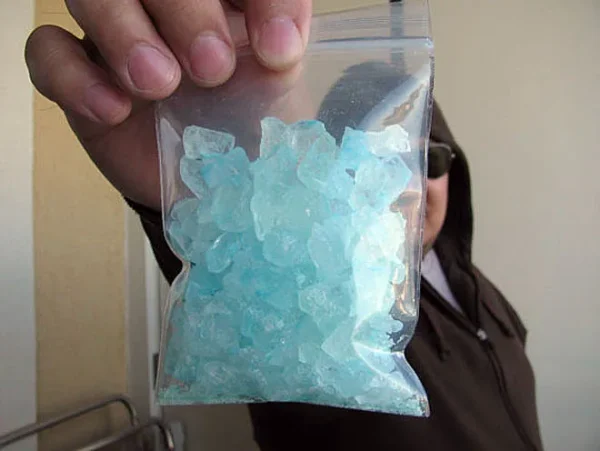
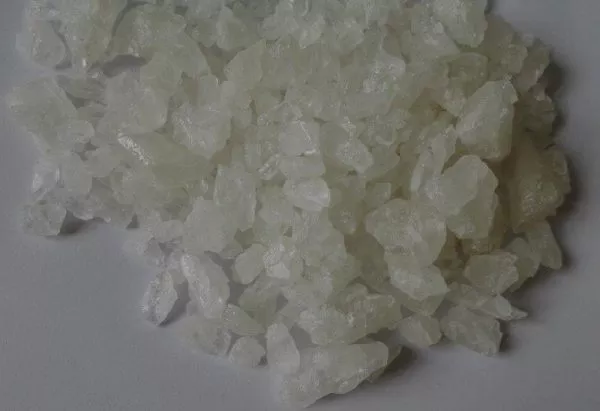
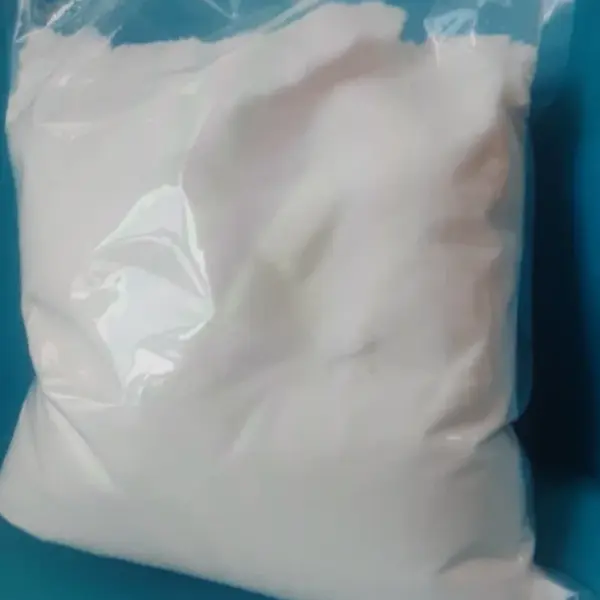
5-CL-ADB-A is classified as an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid, distinctly characterized by its unique chemical structure. This compound belongs to a broader family of synthetic cannabinoids, which are designed to mimic the psychoactive effects of naturally occurring cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. The molecular formula of 5-CL-ADB-A indicates significant interactions with the cannabinoid receptors, notably the CB1 receptor, which is primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects observed with cannabis consumption.
The structural framework of 5-CL-ADB-A can be compared to that of 5F-ADB, another well-known synthetic cannabinoid. The primary distinction between these two compounds lies in the structural modifications that have been made. Notably, the methyl ester present in 5F-ADB is replaced with an amylene chain in 5-CL-ADB-A. This subtle alteration contributes to differences in their pharmacological profiles and potencies, influencing the way they interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system.
The presence of the chlorine atom (Cl), as indicated by the name 5-CL-ADB-A, further differentiates it from its analogs and enhances its affinity for cannabinoid receptors. This halogen addition is significant as it can influence both the lipophilicity and overall stability of the compound, thus affecting its pharmacokinetics and dynamics. In addition, studies have shown that the structural characteristics of indazole cannabinoids, including their nitrogen atom positions, play a crucial role in their binding efficacy and subsequent psychoactive effects.
Understanding the chemistry of 5-CL-ADB-A not only helps elucidate its pharmacological actions but also provides valuable insight into the development of synthetic cannabinoids. As research progresses, the knowledge of such indazole-based compounds continues to grow, paving the way for more extensive studies on their safety, efficacy, and potential therapeutic applications.
5-CL-ADB-A, an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid, interacts primarily with the cannabinoid receptors in the human endocannabinoid system, specifically the CB1 and CB2 receptors. This synthetic compound exhibits a higher potency compared to natural cannabinoids like THC, leading to a more pronounced pharmacodynamic profile. The binding mechanism of 5-CL-ADB-A mimics that of endogenous cannabinoids, activating these receptors and eliciting a range of physiological responses.
Upon binding to the CB1 receptors predominantly located in the central nervous system, 5-CL-ADB-A can induce psychoactive effects such as euphoria, altered perception, and relaxation. These intended effects may resemble those of cannabis, making it appealing for users seeking similar experiences. Conversely, the potency of 5-CL-ADB-A can also lead to adverse reactions. Short-term effects may include anxiety, paranoia, and confusion, which are often reported with synthetic cannabinoids due to their unpredictable nature. Furthermore, users may experience increased heart rate, dry mouth, and dizziness, which are common side effects associated with cannabinoid receptor activation.
Long-term effects of 5-CL-ADB-A are still primarily unknown, as research on this compound remains limited. However, there is growing concern regarding potential dependency and withdrawal symptoms due to the compound’s synthetic nature and high potency. Continued use may lead to tolerance development, where users may find themselves requiring higher doses to achieve similar effects. Additionally, there is a risk of detrimental impacts on cognitive function and mental health, thus highlighting the need for a comprehensive understanding of this substance.
Overall, understanding how 5-CL-ADB-A interacts with cannabinoid receptors is crucial in gauging both its therapeutic potential and health risks, emphasizing why further research into its pharmacodynamics and long-term effects is essential.
The legal status of 5-CL-ADB-A, an indazole-based synthetic cannabinoid, varies significantly across different regions, reflecting the broader complexities surrounding the regulation of novel psychoactive substances. In many jurisdictions, synthetic cannabinoids remain largely unregulated, allowing for the sale and distribution of 5-CL-ADB-A through various online platforms. However, as awareness of the potential risks and implications of these substances increases, a growing number of countries have begun to implement specific regulations targeting such compounds.
In the United States, for example, 5-CL-ADB-A is not specifically listed as a controlled substance under federal law; however, its classification may fall under the more general regulations set forth by the Federal Analog Act. This statute essentially dictates that any substance chemically similar to a controlled substance and intended for human consumption can be prosecuted. As the legal landscape evolves, states are also enacting their own laws, which may list synthetic cannabinoids, including 5-CL-ADB-A, as illegal substances.
On the international front, many European countries have included contents of indazole and similar structures in their drug control legislation, categorizing them as controlled substances. This has resulted in 5-CL-ADB-A being banned in several nations, contributing to a patchwork of regulations. In contrast, regions with limited regulatory frameworks may still allow the unregulated sale of 5-CL-ADB-A, often through online retailers. These platforms frequently utilize discreet shipping methods and cryptocurrencies to facilitate transactions, further complicating enforcement efforts for regulatory bodies.
The challenge for regulators lies not only in closing the loopholes but also in addressing the public health risks associated with the unregulated market for synthetic cannabinoids such as 5-CL-ADB-A. The rapid proliferation of such substances poses significant difficulties in monitoring their distribution and understanding their effects, necessitating robust legal frameworks and public awareness campaigns to protect consumers. The ongoing evolution of the market will require vigilant attention from authorities to balance regulation and health considerations effectively.
The use of synthetic cannabinoids, such as 5-CL-ADB-A, presents a range of significant risks and considerations for potential users. One primary concern revolves around the health effects stemming from these substances, which are often unpredictable and can vary significantly from user to user. Unlike traditional cannabis, which has been studied more thoroughly and is understood to have certain effects, synthetic cannabinoids can provoke severe adverse reactions, including anxiety, paranoia, and hallucinations. Furthermore, the legal and unregulated status of products containing 5-CL-ADB-A means that users frequently encounter unknown variables in product potency and composition, which can lead to overdose or other serious health consequences.
Addiction is another critical consideration concerning the use of 5-CL-ADB-A. Users may find themselves developing a tolerance, leading them to consume higher doses to achieve the desired effects. This pattern can precipitate psychological dependence over time. While many may view synthetic cannabinoids as a safer alternative to traditional cannabis, the reality is that the risk of addiction and other mental health issues is comparable or even greater with substances like 5-CL-ADB-A, especially given their unpredictable nature.
Furthermore, the variability in product quality is a significant concern, as many synthetic cannabinoids are produced in uncontrolled settings. This lack of oversight can lead to product contamination or mislabeling, which heightens the risk of adverse effects. To mitigate these risks, harm reduction strategies are vital. Users should be educated on the dangers of synthetic cannabinoids and the importance of sourcing products through reliable and reputable vendors, if available. Awareness campaigns can play a significant role in informing users about the differences and dangers of synthetic cannabinoids compared to traditional cannabis products, ultimately promoting safer choices in their use.