$280.00 – $8,500.00Price range: $280.00 through $8,500.00
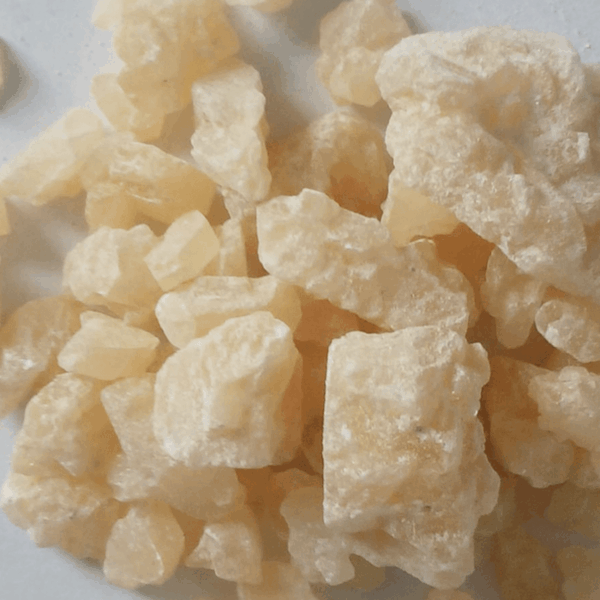
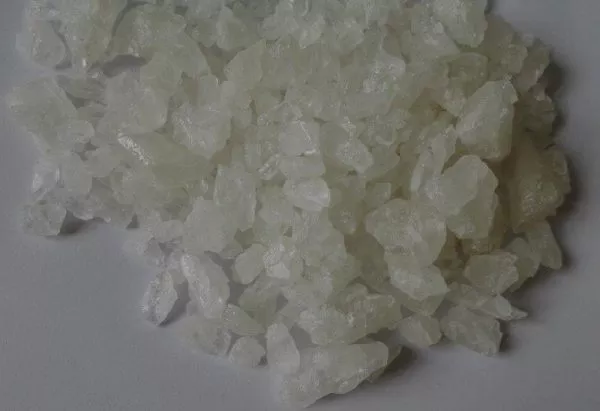
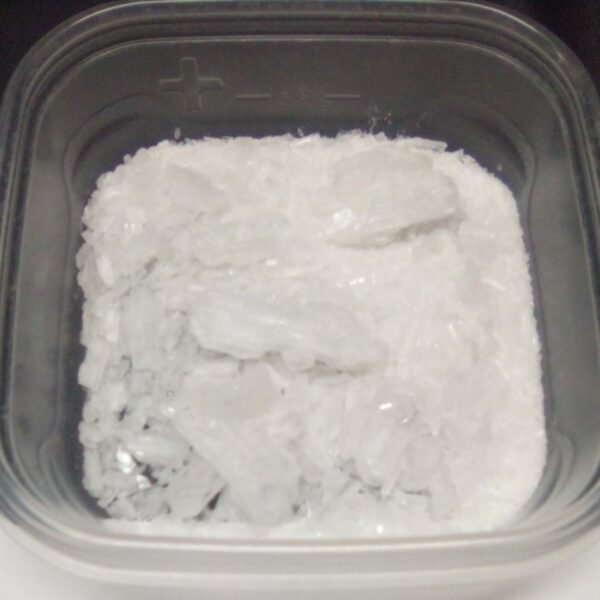
Crystal meth, scientifically known as methamphetamine, is a powerful and highly addictive central nervous system stimulant. Its chemical structure is classified as a phenethylamine derivative, which allows it to induce heightened levels of dopamine within the brain, leading to intense feelings of euphoric pleasure. Typically, this substance appears in crystalline form, resembling clear or bluish-white rocks, which differentiate it visually from other forms of methamphetamine.
The production of crystal meth primarily involves chemical synthesis from readily available precursors such as pseudoephedrine, commonly found in over-the-counter cold medications. This illicit manufacturing process often takes place in makeshift laboratories, where basic household products are repurposed into dangerous and highly potent chemicals. The illicit nature of its production contributes to varying purity levels; however, crystal meth is known for its remarkably high purity, often exceeding 90% and reaching up to 97%. This high purity level significantly heightens its addictive potential and increases the risks associated with its use.
Common methods of consumption include smoking, snorting, injecting, or swallowing the substance. Smoking is perhaps the most prevalent method, as it allows for rapid absorption into the bloodstream, intensifying its effects. Alternatively, injection provides a direct route for the drug to enter the bloodstream, leading to even more immediate and powerful euphoria. The various consumption methods reflect users’ attempts to maximize the drug’s effects, accompanied by an increased risk of overdose due to the potency of 97% pure methamphetamine.
Understanding the composition, production, and consumption methods of crystal meth is crucial in grasping its risks and implications. The staggering purity level marks a distinct difference between crystal meth and other forms of methamphetamine, underscoring the serious health consequences associated with its use.
Engaging in the purchase of crystal methamphetamine carries significant risks that should not be underestimated. Firstly, the legal ramifications associated with the possession, distribution, and use of this substance can be severe. In many jurisdictions, crystal meth is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance, which means that its unauthorized distribution or possession can lead to serious criminal charges. Offenders may face hefty fines, prolonged incarceration, or both, depending on the quantity involved and the specific laws of the area. Therefore, individuals contemplating the purchase of crystal meth must be acutely aware of the legal implications involved in their actions.
Health risks associated with crystal meth use also pose a critical concern. This stimulant has a high potential for physical dependence and addiction, which can lead to devastating consequences for both physical and mental health. Users often experience increased heart rates, elevated blood pressure, and heightened body temperature, all of which can result in serious medical emergencies. Prolonged use can cause significant damage to the brain, affecting cognitive functions and emotional regulation. Additionally, the likelihood of developing psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, paranoia, or hallucinations increases with continued use, leading to a cycle of dependency that can be challenging to break.
Moreover, the safety concerns surrounding the purchase of crystal meth cannot be overstated. Buyers often engage with illicit markets that operate without regulation and oversight. This could expose them to additional dangers such as violence, exploitation, and compromised safety in transactions. Furthermore, the purity of the drug can vary significantly between batches; hence, users may unknowingly purchase products mixed with harmful adulterants that can exacerbate the health risks and further jeopardize their well-being.
Crystal methamphetamine, commonly known as crystal meth, is a powerful and highly addictive stimulant. The short-term effects of using crystal meth can manifest very quickly, often producing a euphoric high characterized by heightened energy, increased alertness, and enhanced sociosexual proclivity. Users may experience a surge of confidence and vigor, leading them to engage in activities that they might typically avoid. This initial phase can also result in decreased appetite, enabling users to forego food for extended periods. However, these seemingly positive effects are deceptive and can rapidly turn into negative experiences.
As the use of crystal meth continues, the psychological implications become increasingly severe. Users often report heightened levels of anxiety, agitation, and paranoia. The drug alters brain chemistry, impacting neurotransmitter systems associated with mood and behavior. Over time, many users may experience significant cognitive decline, making concentration and memory retrieval challenging. This decline often leads to social withdrawal as individuals become increasingly isolated due to their mental health decline.
Furthermore, the risk of overdose is one of the most dangerous consequences of crystal meth use. The potency of 97% pure methamphetamine raises the likelihood of lethal outcomes when consumed, especially when combined with other substances. Symptoms of an overdose may include increased heart rate, overheating, and seizures, which can potentially lead to death. Understanding the comprehensive impacts of crystal meth on both the body and the mind is crucial in grasping its perilous nature. The implications of usage extend well beyond physical effects and encapsulate damaging psychological effects that can alter one’s life trajectory.
Addiction and dependence are two critical concepts often associated with substance use disorders, including those involving crystal methamphetamine. Addiction is defined as a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, continued use despite harmful consequences, and long-lasting changes in the brain’s structure and function. Dependence, on the other hand, refers to the state in which an individual requires the substance to function normally, experiencing withdrawal symptoms when not using it. Both conditions are intricately linked in the context of crystal meth use.
Crystal meth, especially the 97% pure form, is highly addictive due to its intense effects on the brain’s reward system. When consumed, it increases the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, leading to feelings of euphoria. This euphoric state can create strong cravings for repeated use, paving the way for addiction. Various factors contribute to the development of methamphetamine addiction, including genetic predispositions, environmental influences, and psychological conditions. For instance, individuals with a family history of substance abuse may be more susceptible to addiction. Additionally, environments characterized by instability, stress, or peer pressure can contribute significantly to the likelihood of developing dependence on crystal meth.
Psychological factors, such as pre-existing mental health disorders, can also play a crucial role. Many individuals use meth as a form of self-medication to cope with symptoms of anxiety, depression, or trauma, which can further entrench their usage patterns. Over time, the body adapts to the presence of crystal meth, leading to physical dependence. Withdrawal symptoms, which may include fatigue, depression, and intense cravings, present substantial challenges for recovery. These symptoms can create a cycle of relapse, making it imperative for individuals seeking to overcome crystal meth addiction to access comprehensive treatment and support systems.
Addressing crystal meth addiction requires a multifaceted approach that accommodates the complexities of the disorder. Numerous treatment options are designed to support individuals as they navigate their recovery journey. One primary method of treatment is behavioral therapy, which concentrates on modifying the thought patterns and behaviors associated with substance use. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective, helping patients identify triggers, develop coping strategies, and manage cravings. Evidence has shown that these therapeutic interventions can significantly improve outcomes for individuals struggling with addiction.
In addition to behavioral therapies, support groups play a crucial role in the recovery process. Programs like Crystal Meth Anonymous (CMA) provide a platform for individuals to share experiences, gain peer support, and build a community that fosters recovery. These groups operate on principles of anonymity and mutual support, emphasizing the importance of connection with others who understand the challenges of addiction. Engaging in a supportive environment can enhance motivation and accountability among individuals seeking to overcome their addiction to crystal meth.
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is another viable option for some individuals, particularly those experiencing co-occurring mental health disorders such as depression or anxiety. While there is no specific medication approved solely for crystal meth dependence, certain medications may alleviate withdrawal symptoms and cravings, making the recovery process more manageable. Healthcare providers can conduct thorough assessments to identify the most suitable approach for each individual, ensuring that treatment is tailored to their unique needs.
Ultimately, it is crucial to recognize that recovery from crystal meth addiction is achievable. With appropriate treatment options and a robust support network, individuals can regain control over their lives and work toward sustained sobriety. Seeking help is a vital first step in overcoming the complexities of addiction. Various resources and support systems are available, demonstrating that hope and healing are within reach for those affected.